Description
Explore the roots, effects, and future of neoliberalism in today’s society.
Introduction

The introduction of this ideology has profoundly reshaped global economies and societies over the past few decades. Originating from economic theories that emphasize free markets, deregulation, and privatization, it has led to significant social and economic changes.
However, its impact has sparked widespread debate, with critics pointing to increased inequality, weakened public services, and diminished democratic processes.
Neoliberalism has turned everyone and everything into a commodity to be traded for profit regardless of the impact on people or the environment.
This comprehensive guide delves into the origins, implementation, impacts, critiques, and future of neoliberalism to provide a thorough understanding of this influential ideology.
The Origins of Neoliberalism
2.1 Historical Context

– Early Development: This ideology appeared in the mid-20th century, influenced by economists like Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman. They advocated for minimal government intervention in the economy.
– Mont Pelerin Society: Founded in 1947, this group of intellectuals championed free-market principles, laying the groundwork for neoliberal policies.
– Key Figures: Hayek and Friedman argued that government regulation stifled economic freedom and innovation, promoting the idea that markets should be self-regulating.
2.2 Core Principles
– Free Markets: Emphasizes the efficiency of free markets in distributing resources and driving economic growth.
– Deregulation: Reducing government intervention in industries to foster competition and innovation.
– Privatization: Transferring public services and assets to the private sector to increase efficiency and reduce public expenditure.
– Government’s Role: Limiting government’s role to keeping law and order, protecting property rights, and ensuring a stable currency.
Neoliberalism in Practice
3.1 Global Implementation
– United States and United Kingdom: Neoliberal policies were prominently implemented during the Reagan administration in the US and Thatcher’s government in the UK. Both leaders reduced taxes, deregulated industries, and privatized public services.
– Developing Countries: The IMF and World Bank promoted neoliberal reforms in developing nations through structural adjustment programs, often leading to significant socio-economic changes.
3.2 Economic Policies
– Deregulation: Industries like finance, telecommunications, and transportation were deregulated to promote competition.
– Tax Cuts: Tax policies favoured the wealthy, reducing tax burdens on corporations and high-income individuals to spur investment.
– Trade Liberalization: Removing trade barriers to integrate global markets, encouraging international trade and investment.
Neoliberalism in Australia
4.1 Implementation of Neoliberal Policies
 – Economic Reforms: Australia embraced neoliberalism in the 1980s, with significant economic reforms under Prime Minister Bob Hawke and Treasurer Paul Keating. These reforms included deregulation of the financial sector, floating the Australian dollar, and privatizing state-owned enterprises.
– Economic Reforms: Australia embraced neoliberalism in the 1980s, with significant economic reforms under Prime Minister Bob Hawke and Treasurer Paul Keating. These reforms included deregulation of the financial sector, floating the Australian dollar, and privatizing state-owned enterprises.
– Workplace Relations: The introduction of enterprise bargaining aimed to increase flexibility and productivity but also weakened collective bargaining and labor unions.
– Public Services: Privatization and outsourcing of public services, including healthcare and education, were pursued to increase efficiency but often led to higher costs and reduced access.
4.2 Social and Economic Impacts in Australia
– Economic Growth and Inequality: While neoliberal policies contributed to economic growth, they also worsened income inequality and wealth concentration.
– Impact on Workers: Casualization and part-time work increased, reducing job security and benefits for many workers.
– Public Sector: Cuts in public spending and privatization led to a decline in the quality and accessibility of essential services.
Social and Economic Impacts
5.1 Economic Inequality
– Wealth Concentration: Neoliberal policies have led to significant wealth accumulation among the elite, widening the gap between the rich and poor.
– Middle-Class Decline: Stagnant wages and rising costs of living have eroded the middle class, contributing to social and economic instability.
5.2 Labor Market Changes
– Gig Economy: The rise of part-time, temporary, and freelance work has increased job insecurity and reduced benefits for workers.
– Workers’ Rights: Neoliberalism’s emphasis on flexibility and competition has often undermined labor rights and collective bargaining power.
5.3 Public Services

– Privatization: Privatizing healthcare, education, and other services has often led to reduced access and quality for the average citizen.
– Social Safety Nets: Reduced government spending on social programs has weakened support for the vulnerable populations.
Neoliberalism and Politics
6.1 Influence on Political Systems
– Corporate Influence: Increased corporate donations and lobbying have given businesses significant power in shaping policies.
– Democratic Erosion: Neoliberalism has sometimes led to the erosion of democratic processes, with power concentrated in the hands of a few.
6.2 Public Perception and Backlash
– Populist Movements: Growing dissatisfaction with neoliberal policies has fuelled populist movements advocating for more fair policies.
– Public Discontent: Widespread protests and political unrest highlight the public’s frustration with economic and social inequalities.
Critiques of Neoliberalism
7.1 Economic Critiques
– Unsustainable Growth: Critics argue that neoliberalism prioritizes short-term gains over long-term sustainability, leading to financial crises.
– Market Failures: Neoliberalism often ignores market failures, such as monopolies and environmental degradation, which require government intervention.
7.2 Social Critiques
– Social Inequality: Neoliberal policies have worsened social inequality, reduced social mobility, and increased poverty.
– Environmental Impact: Deregulation and emphasis on economic growth have often led to environmental degradation and climate change.
The Future of Neoliberalism
8.1 Emerging Alternatives
– Progressive Policies: There is a growing push for policies that prioritize social equity, environmental sustainability, and inclusive growth.
– Reimagining Public Services: Advocates call for strengthening public services and social safety nets to ensure access and quality for all citizens.
8.2 Replacing “Free Trade” with “Fair Trade”
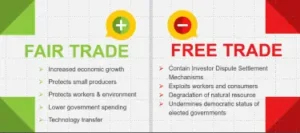
– Concept of Fair Trade: Fair trade emphasizes fair trading practices, ensuring fair wages and working conditions for workers, particularly in developing countries.
– Benefits of Fair Trade: Promotes sustainable development, reduces exploitation, and supports local economies.
– Implementing Fair Trade: Encouraging policies that prioritize fair wages, ethical sourcing, and sustainable practices over pure market liberalization.
8.3 Pathways to Change
– Strengthening Democracy: Enhancing democratic institutions to ensure fair representation and reduce corporate influence.
– Sustainable Models: Promoting economic models that balance growth with social and environmental responsibilities.
Conclusion
Neoliberalism has profoundly changed global economies and societies, reshaping industries, labor markets, and public services. While it has driven economic growth and innovation, it has also led to increased inequality, weakened public services, and challenges to democratic processes. As the world grapples with these issues, emerging alternatives, and pathways to change offer hope for a more fair and sustainable future.
Thought-Provoking Question
How has neoliberalism changed your life, and what changes would you like to see in economic policies?
Call to Action
Stay informed about economic and social policies. Join the conversation and share your thoughts on how we can move towards a fairer society.
Social Sharing
Share this article to spread awareness and foster discussions on neoliberalism and its impact.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deep understanding of this ideology, its roots, impacts, and future, helping readers navigate the complexities of this influential ideology.

