
Description:
Explore freedom in Australia through neoliberalism vs. equal opportunity, focusing on economic, political, and social impacts.
Introduction
Freedom is often championed by politicians, but what does it truly mean? In Australia, the term “freedom” is frequently associated with neoliberal ideals, emphasizing market freedom and minimal government intervention. However, this perspective often overlooks the broader concept of freedom—one that ensures every individual has an equal opportunity to thrive.
Neoliberalism has shaped Australian policies for decades, prioritizing economic freedom for individuals and businesses. But has this focus on market-driven freedom led to a more equitable society? Many Australians find themselves questioning whether the current model of freedom truly benefits everyone or simply perpetuates inequality.
This article will explore freedom in Australia from two perspectives: neoliberal ideology and the broader concept of freedom as equal opportunity. By examining the economic, political, and social impacts of each approach, readers will gain a deeper understanding of how these differing views shape Australian society.
1. Neoliberal Ideological Perspective on Freedom
1.1 Core Principles of Neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is rooted in the belief that individual freedom is best achieved through free markets and minimal government intervention. The ideology champions the idea that economic success is a product of personal responsibility and competition, with the market acting as the ultimate arbiter of value. Neoliberal thinkers argue that the less the government interferes, the more freedom individuals have to pursue their interests.
1.2 Economic Freedom
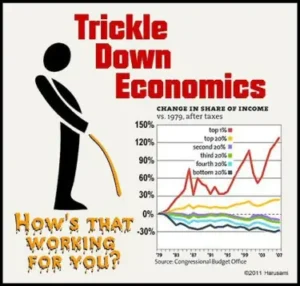
Economic freedom is at the heart of neoliberalism. In this view, freedom is synonymous with the ability to engage in economic activities without undue government restriction. This perspective has led to policies favoring deregulation, privatization of public services, and tax cuts for businesses and high-income earners. The underlying belief is that a free market will naturally lead to prosperity for all, with wealth trickling down to the broader population.
1.3 Political Freedom
Neoliberalism also emphasizes political freedom, particularly in terms of reducing government influence over individual lives. This includes limiting the role of government in regulating businesses and personal behavior. The focus is on protecting property rights, promoting free speech, and ensuring that individuals can make their own choices without state interference. However, critics argue that this form of political freedom often benefits the wealthy and powerful, who have the resources to influence political outcomes.
1.4 Social Freedom
In the neoliberal framework, social freedom is linked to the idea of choice and competition in sectors like education and healthcare. Neoliberal policies often promote the privatization of these services, arguing that competition will lead to higher quality and greater efficiency. However, this approach can lead to disparities in access and quality, with those unable to afford private options being left behind.
2. Consequences of Neoliberal Freedom in Australia
2.1 Economic Inequality
One of the most significant consequences of neoliberal freedom in Australia is the rise in economic inequality. As wealth and resources become concentrated in the hands of a few, the gap between the rich and poor widens. Neoliberal policies, such as tax cuts for the wealthy and the privatization of essential services, exacerbate this divide, leading to a society where freedom is increasingly limited to those with economic power.
2.2 Social Fragmentation
Neoliberalism’s focus on individualism and competition has contributed to social fragmentation in Australia. As public services are privatized and community support systems erode, individuals are left to fend for themselves in an increasingly competitive environment. This shift undermines social cohesion, leading to a society where the sense of community and mutual support is diminished.
2.3 Impact on Democracy
Neoliberal freedom has also had a profound impact on Australian democracy. As corporate interests gain greater influence over political decision-making, the voice of ordinary citizens is often drowned out. This erosion of democratic freedoms is particularly evident in policies that prioritize the interests of businesses and the wealthy over those of the broader population. The result is a political system that increasingly serves the few rather than the many.
3. Freedom as Equal Opportunity for All
3.1 Defining Freedom Beyond the Market

Freedom, in its fullest sense, extends beyond the narrow confines of market-driven success. It encompasses the ability to access essential resources, live a life of dignity, and participate fully in society. This broader conception of freedom recognizes that true liberty involves more than just the absence of government interference; it requires the presence of opportunities for all individuals to thrive.
3.2 Economic Justice
Economic justice is central to the idea of freedom as equal opportunity. This perspective argues that the government has a crucial role in ensuring that wealth and resources are distributed fairly across society. Policies that support economic justice include progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and investments in public services such as education, healthcare, and housing. These measures aim to level the playing field, giving everyone the chance to succeed, regardless of their economic background.
3.3 Social Equity
Social equity is another key component of freedom as equal opportunity. This concept involves ensuring that all individuals have access to the same quality of essential services, regardless of their socio-economic status. Publicly funded healthcare, education, and housing are critical to achieving social equity. When these services are available to all, individuals have the freedom to pursue their goals and contribute to society without being held back by systemic barriers.
3.4 Political Empowerment
Political empowerment is vital to ensuring that freedom is more than just a theoretical concept. It involves expanding democratic participation and reducing the influence of money in politics. Policies that promote political empowerment include campaign finance reform, voting rights protections, and efforts to increase civic engagement. When all citizens have a voice in the political process, freedom becomes a reality for everyone, not just the privileged few.
4. Comparative Analysis
4.1 Freedom Under Neoliberalism vs. Equal Opportunity
When comparing freedom under neoliberalism with freedom as equal opportunity, it becomes clear that these two perspectives lead to vastly different outcomes. Neoliberal freedom often prioritizes market success and individual competition, leading to increased inequality and social fragmentation. In contrast, a model of freedom that emphasizes equal opportunity seeks to create a more just and equitable society, where everyone has the chance to succeed.
4.2 Case Studies
To illustrate these differences, we can look at specific examples from Australian history and policy. The privatization of essential services, such as healthcare and education, under neoliberal policies has often led to disparities in access and quality. On the other hand, policies that focus on equal opportunity, such as the introduction of Medicare and public education reforms, have helped to level the playing field and provide greater freedom for all Australians.
5. The Australian Context
5.1 Historical Overview
Australia’s embrace of neoliberal policies began in the 1980s, with a shift towards deregulation, privatization, and a reduction in the role of government. These policies were championed as a means of increasing economic freedom and driving growth. However, over time, the limitations of this approach have become apparent, particularly in terms of rising inequality and social division.
5.2 Current State
Today, Australia finds itself at a crossroads. While neoliberalism continues to influence policy decisions, there is growing recognition of the need for a more balanced approach that prioritizes social equity and economic justice. Public opinion is increasingly shifting towards a model of freedom that includes equal opportunity for all, as evidenced by debates over issues such as wealth inequality, access to healthcare, and the influence of corporate interests on democracy.
6. Conclusion
6.1 Summary of Key Points
This article has explored two contrasting visions of freedom in Australia: the neoliberal perspective, which emphasizes market-driven success and individual competition, and the concept of freedom as equal opportunity for all. While neoliberalism has been successful in promoting economic growth, it has also led to significant social and economic challenges, including rising inequality and a weakening of democratic institutions. In contrast, a model of freedom that prioritizes equal opportunity seeks to create a more just and inclusive society.
6.2 Future Outlook
As Australia continues to grapple with the consequences of neoliberal policies, there is an opportunity to redefine freedom in a way that ensures all citizens have the chance to thrive. By embracing policies that promote economic justice, social equity, and political empowerment, Australia can create a society where freedom is not just the privilege of the few but a right for all.
6.3 Call to Action
Readers are encouraged to advocate for a broader understanding of freedom, one that includes equal opportunity for all Australians. This can be achieved by supporting policies that promote social equity, economic justice, and democratic participation. By doing so, we can help to create a society where everyone has the freedom to live a life of dignity and purpose.
Question for Readers
How do you define freedom in your own life, and do you believe that Australia’s current approach truly allows everyone the chance to thrive?
Social Sharing
If you found this article insightful, please share it on your social media platforms to help spread the message.
