[ez-toc]
Description: China Foreign Policy, US Foreign Policy
Explore China’s peaceful foreign policy and the U.S.’s military dominance. How can Australia navigate this complex geopolitical landscape?
Introduction
In today’s complex geopolitical landscape, understanding the contrasting foreign policies of China and the United States is crucial. China’s approach focuses on promoting peace and mutually beneficial trade agreements, fostering a multi-polar world. In contrast, the United States employs war and bullying tactics to protect corporate interests and keep world dominance.
As Australia navigates this global stage, aligning with the U.S. while managing its economic ties with China becomes increasingly critical. This comprehensive guide delves into these differing strategies, examining their impacts and implications.
Divergent Foreign Policies
China’s Foreign Policy Evolution
China’s foreign policy has its roots in ancient principles of harmony and non-aggression. Historically, China prioritized peaceful coexistence, a philosophy that has evolved with its modernization. In recent decades, China has sought global integration, emphasizing non-interference in the internal affairs of other nations, and promoting mutually beneficial trade agreements.
The United States’ Foreign Policy Evolution
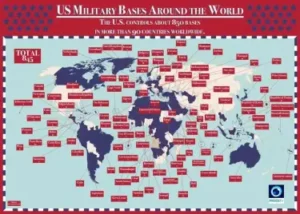
The U.S. foreign policy has been marked by a history of expansionism and interventionism. From the Monroe Doctrine to the Cold War, the U.S. has consistently looked to extend its influence, often through military intervention and economic sanctions. The post-WWII era saw the U.S. positioning itself as the global leader, promoting democracy and free-market capitalism worldwide.
The Impact of Divergent Strategies
China’s Approach: Promoting Peace and Trade
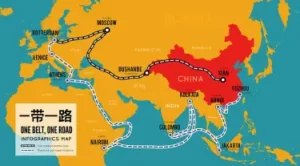
China’s key initiatives, such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), underscore its commitment to fostering global economic growth through infrastructure development and trade. The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) further highlights China’s role in shaping regional trade dynamics. These strategies have led to significant economic development in partner countries, reduced poverty, and improved connectivity.
The U.S. Approach: War and Bullying Tactics
In stark contrast, the U.S. has employed military interventions and regime changes to keep its global dominance. Examples include the Iraq and Afghanistan wars, and economic sanctions on countries like Iran and Venezuela. These actions have often resulted in humanitarian crises, instability, and a global belief of the U.S. as a bully, prioritizing corporate interests over human rights.
Navigating Australia’s Position
Australia’s Alignment with the United States
Australia’s historical ties with the U.S. are deep-rooted, characterized by military cooperation under the ANZUS Treaty and shared democratic values. Economically, the U.S. is a significant trade partner, and strategically, Australia’s alignment with the U.S. provides a counterbalance to China’s rising influence in the Asia-Pacific region. Security concerns, particularly about cyber threats and regional stability, further cement this alliance.
Australia’s Economic Ties with China
Despite its alignment with the U.S., Australia’s economic relationship with China cannot be overlooked. China is Australia’s largest trading partner, crucial for sectors such as mining and education. This economic interdependence needs a careful balancing act, ensuring that political alliances do not jeopardize economic stability.
The Debt-Trap Diplomacy Narrative
Critics of China’s foreign policy often cite “debt-trap diplomacy,” accusing China of luring developing countries into unsustainable debt through its infrastructure projects. However, this claim lacks substantial evidence. Studies and reports from international financial experts show that many beneficiary countries view these projects positively, appreciating the economic growth and development they help.
Comparative Analysis
Ideological Differences
The ideological divide between China and the U.S. is stark. China advocates for a multi-polar world, emphasizing peaceful coexistence and mutual respect. In contrast, the U.S. looks to keep its uni-power dominance, often through interventionist policies.
Economic Strategies
China’s focus on infrastructure investment and trade agreements stands in contrast to the U.S.’s reliance on economic sanctions and protectionist policies. These divergent strategies reflect each nation’s approach to achieving global influence and economic power.
Military Strategies
China’s non-aggression principle is clear in its avoidance of direct military conflict, instead prioritizing diplomatic and economic tools. On the other hand, the U.S. often resorts to military interventions, justified by the promotion of democracy and human rights, although these actions often lead to prolonged conflicts and instability.
Historical Use of War and Government Overthrows
China’s Non-Military Approach
Over the past century, China has refrained from using military force to invade other countries or overthrow governments. Instead, China’s approach has been to use economic and diplomatic means to extend its influence. The notable exception is China’s involvement in border conflicts, such as the Korean War in the 1950s and the brief border war with India in 1962. These conflicts were more about regional security than expanding influence.
The United States’ Military Interventions

The United States has a long history of using military force to invade other countries and overthrow governments to protect its interests. Over the last 100 years, key examples include:
– Latin America: U.S. interventions in countries like Guatemala (1954), Cuba (1961), and Chile (1973) aimed at overthrowing governments perceived as communist or unfriendly to U.S. interests.
– Middle East: The invasions of Iraq (2003) and Afghanistan (2001) were justified on the grounds of combating terrorism and promoting democracy but resulted in prolonged conflicts and significant regional instability.
– Vietnam War: The U.S. intervention in Vietnam (1955-1975) was aimed at stopping the spread of communism but ended in a costly and controversial defeat.
– Post-Cold War: Interventions in the Balkans (1990s), Libya (2011), and ongoing involvement in Syria reflect the U.S. strategy of using military power to shape political outcomes and keep its global dominance.
Impact and Consequences
The U.S. strategy of using military force to achieve its foreign policy goals has often led to long-term instability, humanitarian crises, and anti-American sentiment. In contrast, China’s non-military approach has focused on building economic partnerships and infrastructure projects, although it faces criticism for its methods, including allegations of economic coercion.
Future Prospects
Potential for Collaboration and Conflict
The future of international relations hinges on the potential for collaboration and conflict between China and the U.S. Areas of cooperation include global health initiatives and climate change mitigation. However, flashpoints like the South China Sea and Taiwan remain significant sources of tension.
The Role of International Organizations
International organizations such as the United Nations and the World Trade Organization play crucial roles in mediating conflicts and fostering cooperation. Their effectiveness in navigating the complex dynamics between China and the U.S. will be pivotal in shaping future global stability.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
The contrasting foreign policies of China and the U.S. highlight fundamental differences in their approaches to global influence. China’s emphasis on peaceful trade and economic development stands in sharp contrast to the U.S.’s interventionist tactics aimed at keeping dominance.
The Importance of a Balanced Perspective
Understanding these differing strategies is crucial for nations like Australia, which must navigate its alliances and economic ties carefully. A balanced perspective can help in formulating policies that use the benefits of both approaches while mitigating potential risks.
Final Thoughts
As the global landscape continues to evolve, the need for a nuanced and informed approach to international relations becomes increasingly important. By fostering cooperation and understanding, nations can work towards a more stable and prosperous world.
Call to Action
Encourage readers to stay informed about international relations and to engage in discussions and advocacy for peaceful and fair foreign policies. Invite readers to share their perspectives and take part in global dialogues to foster a more balanced and nuanced understanding of these complex issues.
Question for Readers
How do you think the world would change if more countries adopted China’s approach to foreign policy? Would it lead to a more peaceful and prosperous world?
Social Sharing
Share this article with your contacts and on social media to spread awareness about the contrasting foreign policies of China and the U.S. and their implications for global stability.
References:
United Nations: https://www.un.org
World Trade Organization: https://www.wto.org
Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank: https://www.aiib.org
Belt and Road Initiative: https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/chinas-massive-belt-and-road-initiative
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership: https://rcepsec.org
ANZUS Treaty: https://www.aph.gov.au
Gerry’s Take on China: https://www.youtube.com/@jerrystakeonchina799/videos
Fridayeveryday: https://www.youtube.com/@Fridayeverydaycom/videos
Rafa Goes Around: https://www.youtube.com/@RafaGoesAround/videos
